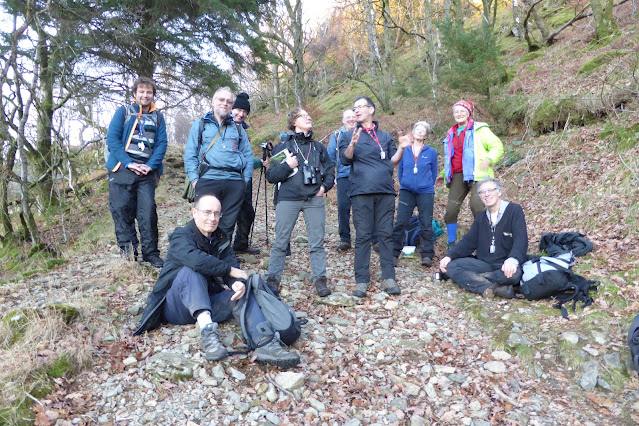
Great How is a small (c330m) but imposing hill at the north end of Thirlmere – map. It’s part of the Thirlmere Woods SSSI, designated for Atlantic bryophytes, with a mix of oak, hazel, birch and ash trees. It was last assessed by Natural England in 2009 when its status was “Unfavourable-Recovering”. Almost all the woodland around the reservoir is non-native conifer plantation but three fragments of old broadleaved trees remain to make up the SSSI. There are ongoing efforts to remove exotic conifers from these woods.
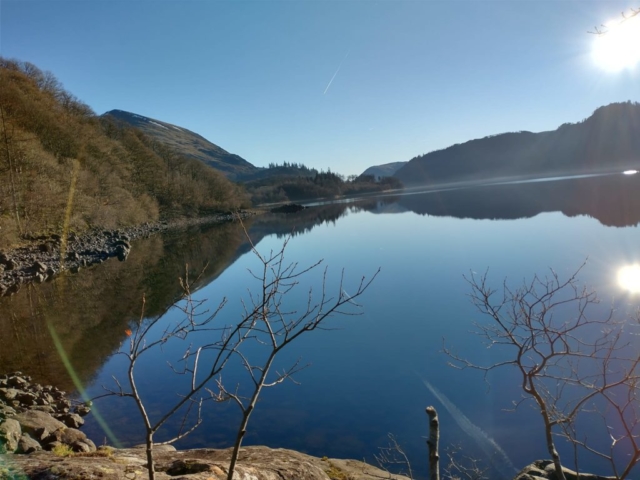
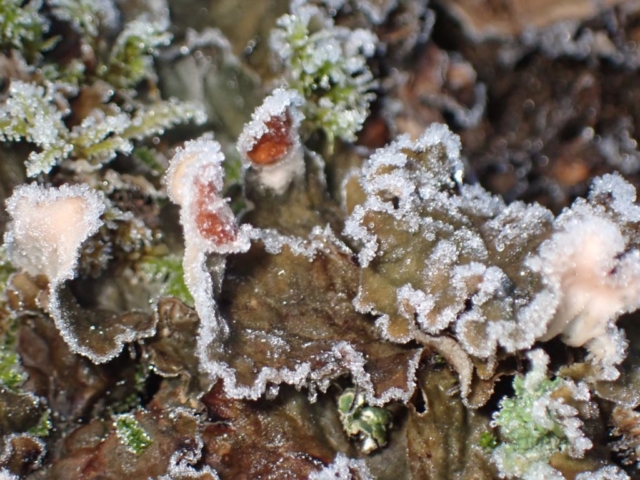
Our route left the minor road by the Thirlmere dam where a footpath skirts the western side of the hill. For once the weather was kind to us – when benign it allows everything to be seen much better in the field, not to mention the enjoyment/comfort factor. The day dawned very cold with frost encrusting the sheets of Peltigera praetextata we saw at the start on the north-facing wall by the road but the mist burned off (it really did) and by lunchtime, when we made it to a south-facing point looking down Thirlmere, it was positively balmy in the sun.
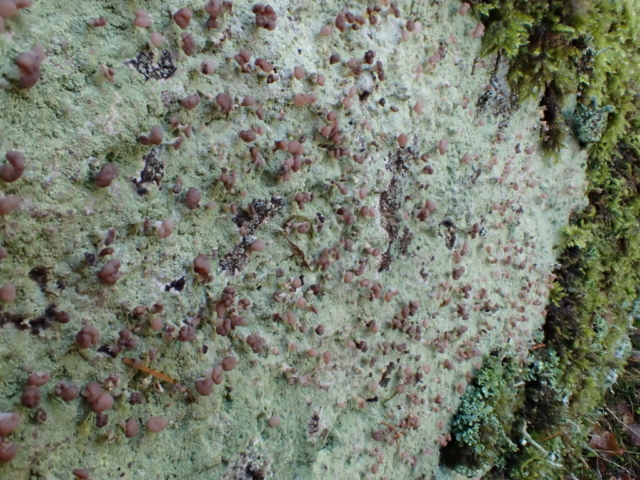
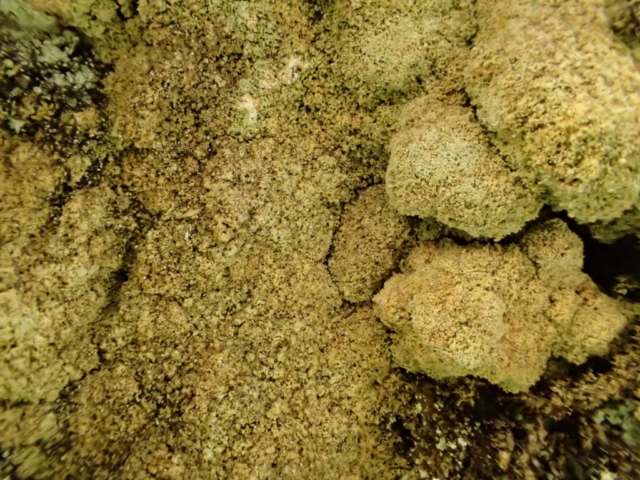
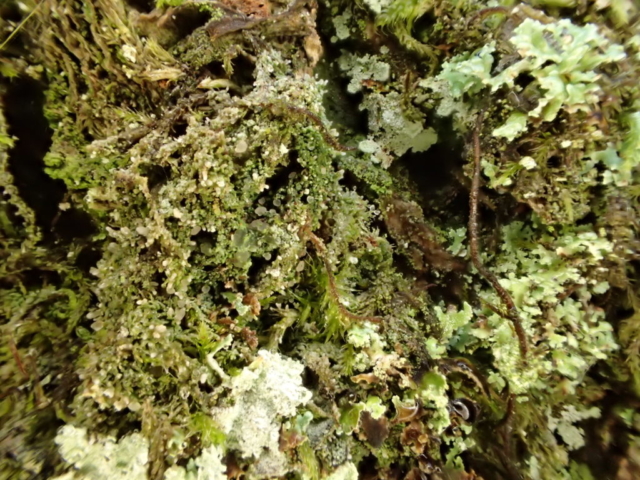
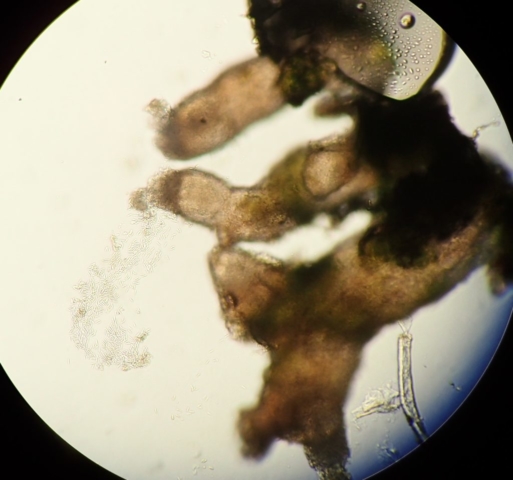
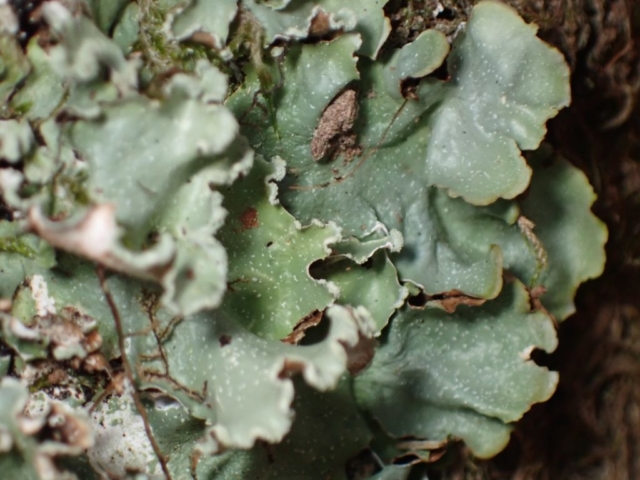
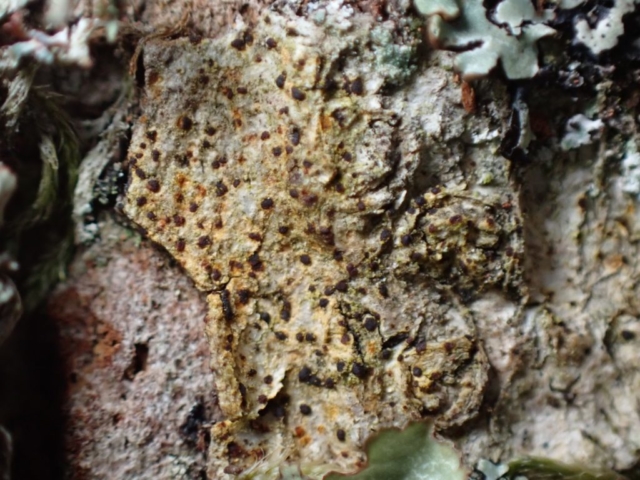
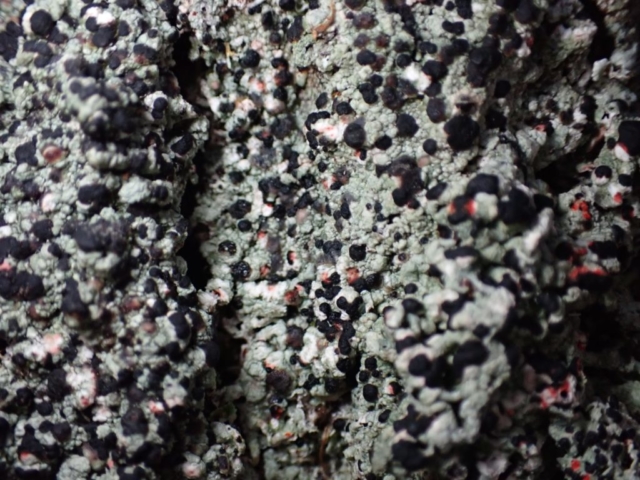
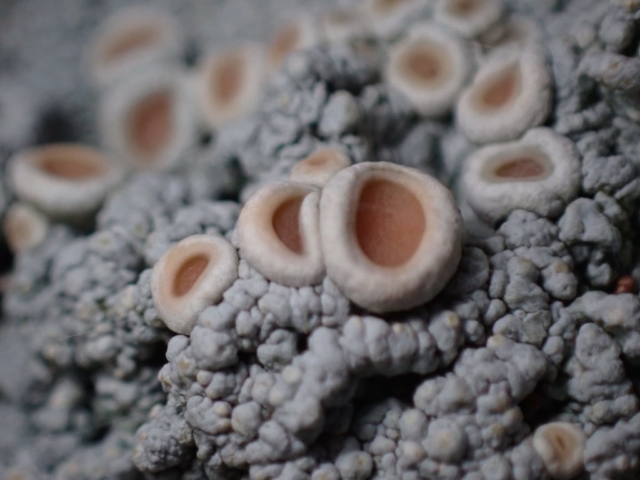
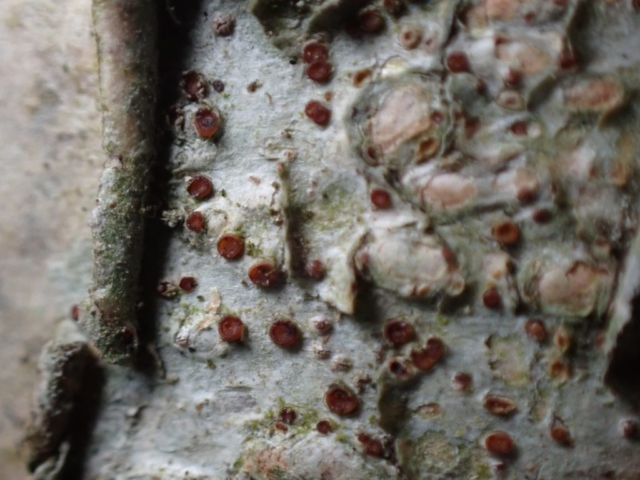
Recent stormy weather had brought many canopy lichens down to the ground for easy viewing so a good range of common acidic bark species were examined. This was great for showing the diversity of lichen morphology to the keen beginners who’d come along. The path skirted some intermittently damp rock faces with interesting crustose species, including the common Baeomyces rufus with pink-brown “mushroom” fruiting bodies, Lepraria membranacea in drier recesses (powdery, yet forming marginal lobe-like structures with upturned rims), red and purple-brown mosaics of Opegrapha gyrocarpa and Enterographa zonata, and a possible example of the rarer Schismatomma umbrinum with a pale brown scurfy crust breaking down into soredia. Close examination of oak trunks nearby revealed a tiny species growing over moss with minute isidia-like structures. Looking under the microscope later these turned out to be pycnidia and we were able to identify this as Micarea stipitata.
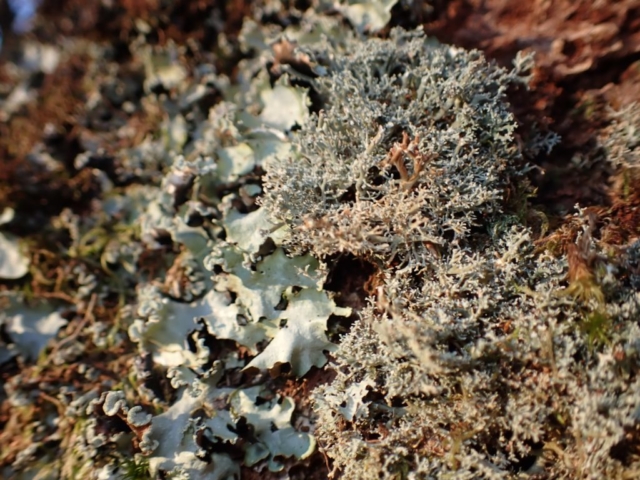
As we got further round the base of the hill the slope above became more gentle so we decided to leave the path and head directly up, examining trees as we went. This was a good move as Cetrelia olivetorum, Arthonia vinosa, Lopadium disciforme and Pachyphiale carneola, the latter on hazel, were found here. After rejoining the track below the summit we refound the copious Bryoria fuscescens seen on our earlier recce, though sadly the old oak had been brought down in the storms. Also near here were Mycoblastus sanguinarius, good quantities of Sphaerophorus globosus and beautiful clear grey-blue patches of Hypotrachyna laevigata, all indicating acidic bark.
There was a total for the day of 68 species. We didn’t visit the steeper areas on the north side of the hill where no doubt further lichens could be found. The east side is mainly a beech plantation and large parts of Great How have in the past been planted with exotic conifers, now slowly being removed with evidence of recent native tree planting. The remaining fragments of good quality old oaks on the western side are a sad reminder of what the wider Thirlmere woods might once have been like before the Sitka monoculture we see today. Hopefully they will survive to help regrow a future oak forest.
Caz Walker
Photos: Pete Martin, Judith Allinson, Clare Shaw and Chris Cant